The PBS program Race of the Power of Illusion is a series that provides lesson plans for teachers of grades 9-14. A series of statements is exemplified by more ambiguous assumptions and stories, each delivered with deep conviction. According to the executive statement, producing this series, it was important to return to the first principles and ask what is this thing called “race?” A question described as so fundamental that it is hardly ever asked. The Human Genome Project answered most of the questions. Project by National-institutes-of-health”>National Institutes of Health, National Human Genome Research Institute produced – “an international research effort to sequence and describe all the genes – together which are the genome – of the members of our species, Homo sapiens.” The only race is the Human race.
The series is online for California Newsreel – three part of the documentary about the nation in society, history and science. Episodes include The Difference Between Us, The Story We Tell and The House We Live In. The program equips students with the background lessons, expertise and resources they seek.
Empirical Challenges to Racial Classification is part of the PBS Program developed by Scott Bronson. Provides lesson plans and resources for teachers to help students examine their preconceptions and assumptions about racial categories and recognize the impossibility of constructing a consistent classification system the human race. ACTIVITY #4: Why Racial Classification Doesn’t Work – Understanding Gradual Variation, Non-Concordance and Within vs. Inter-Group Variation includes films for students to view. For a complete transcript of the episode, click here. One of the groups is compared to the disease silence.
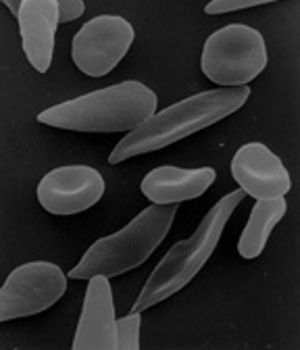
Sickle cell disease is an inherited disorder that affects red blood cells. Sickle cell disease affects more than 72,000 Americans, primarily of African heritage, but also of Arab, Asian, Caribbean, Indian, Mediterranean Italian, Spanish, and Central American descent. The Sickle Cell Handout listed below shows how one group of people migrating from a central location can develop a gene mutation that is passed from generation to generation.
The study investigates the distinct letters of transformation in our genetic code that determine the ability of genes to produce proteins, published on February 5, 2009 in the Journal of Human Genetics. The researchers propose the conclusions that such changes, sometimes harmful, are usually of little importance to the entity and sometimes can be beneficial in terms of development. According to the article of the year hundredth nongentesimi five hundred quingentesimi nongentesimi hundred five hundred five hundred five hundred and thirty-seven can not be turned to our salvation. A study by Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute researchers prompts new research into the effects of weight loss and our evolution our evolution . The DNA sequence of genes can be changed in many ways. There are many types of changes.
Sickle cell anemia is a hereditary disease that results from a single mutation (SNP or single nucleotide polymorphism) in one of the genes that code for the hemoglobin protein in our red bloods Hemoglobin carries oxygen through the blood to the body.
People who inherit two copies of the altered hemoglobin gene, one from each parent, get sickle cell anemia. Their red blood became sticky and stiff, and sometimes shaped like a sickle. These “sick” cells usually stick to blood vessels, which are capillaries, which are blood they obstruct the flow. Sickle cell anemia is a very serious disease and can be life threatening.
But many people who inherit only one copy of the altered gene are known as sickle-cell carriers. They tend not to die and interestingly, sickle cell carriers tend to resist malaria, a deadly disease.
Malaria is caused by a parasite carried by elephants. After humans began to practice agriculture, the mosquito stopped standing in pools of water that appeared on the cleared land. Scientists believe that the sickle cell mutation arose independently from four or five different periods in human history, no more than 10,000 years ago and probably much more recently. Because one sickle cell carrying the gene conferred a survival advantage in regions of the world where malaria was common, sickle cell mutations in those regions were positively selected and passed on.
When humans migrated, the sickle cell trait spread not by infection, of course, but by reproduction. Population geneticists call it ‘gene flow’ when a type of variant passes from one to another like a sickle cell. Due to these historical and environmental influences, the sickle cell is commonly found in central and western Africa, but not in southern Africa. It is also found in the Arabian Peninsula and in India, and throughout Turkey, Greece, Albania, Sicily and Italy and other parts of the Mediterranean basin.
The hemoglobin gene, carrying the sickle cell variant, is not a gene, but a lineage from those who once lived where malaria was common.
According to the CDC, malaria is a disease carried by a mosquito parasite. If not treated, people develop serious complications and die. The CDC says that each year 350-500 million cases of malaria occur worldwide, and over one million people die, most of them children in sub-Saharan Africa.
Here sometimes fatal disease can be prevented and cured. “Because carrying one sickle cell gene conferred a survival advantage in regions of the world where malaria was common, the sickle cell mutation was selected and transmitted in those positive regions.”
Gene flow is the difference in genetic growth in a population. This disturbance occurs because people from other populations will transport alleles from one population to another. The flow of gender affects the similarities and differences between peoples. Gene flow has a tendency to occur in closely related populations, and when it occurs, alleles carried in one population will be introduced into another population. The more gene flow, the more neighboring peoples will become.
Most of our requests are spread around gender mistakes. The people of the world are not biologically distinguished along racial lines. It is in this sense that we hold all notions of race.
Sects of racism are real. In the PBS program, he states that he wants this series to help clear the “biological thicket” and clearly disprove the social, economic and political core that inexplicably drives the “white people”‘s fortunes and misfortunes.
Work Citation:
http://www.pbs.org/race/000_About/002_04-doctores-04.htm
http://www.genome.gov/10001772
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/mutationsanddisorders/possiblemutations
(http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/public/blood/sicle/sca_fact.pdf)
http://www.nationalgeographic.com/xpeditions/lessons/09/g68/tgmigration.html
Report:
- www.pbs.org/race/001_WhatIsRace/001_00- home.htm< /a>
- www.pbs.org/race/005_MeMyRaceAndI/005_00-home.htm< /a>
- www.pbs.org/race/000_About/002_04- teachers.htm< /a>