What is Scabies?
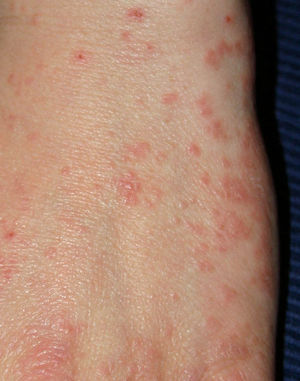
Scabies is a contagious skin rash. The eruption consists of a small pointed vesicle. It appears at first between the fingers, forefingers, feet, male genitalia, inside the joints, and in those parts of the body where the texture of the skin is thin.
It gradually spreads throughout the body, except for the skull and face, which are rarely affected. The disease can spread widely, or remain localized on a small part of the body’s surface. Vesicles usually not bundled. These contain small amounts of clear fluid. A violent desire to itch, add to this inconvenience of illness.
Signs of scabies:
The diagnosis of scabies is often very difficult because its symptoms can easily be mistaken for other conditions itchy skin such as scabies. However, the first and most common symptom of scabies is itching, especially at night.
Swellings that are red in color and blisters also appear insect bites or blisters. As the condition worsens, the skin may become scaly or scaly, especially around the fingers, hands, ankles, buttocks, nipples, and armpits. The infestation in children can occur all over the body, especially on the soles, palms, and hair.
The causative organism of scabies: Sarcoptes scabies is a small insect. The tunnels of the female are gentle on the skin, close to the bladder. In some cases pustules, filled with yellow matter, grow. A little pustule slips out following the path, which lays the eggs in minute tracks.
After a few weeks, each affected person shows an allergic response to the minnow and its eggs. This results in severe scabbing and dew on the site. If left untreated, the eggs hatch and new hatchlings come up and take the cycle forward. In minute scabies arise very persnickety.
warm bodies want to thrive. As a result, the transmission of scabies requires prolonged physical contact. Under the best conditions, scabies can be extremely contagious and can be contaminated by contact with an infected person.
It can take more than a month before the affected person has recognized the signs of infection, especially if the person is health care is maintained. > He has all the time and takes regular baths. It is possible, therefore, that the sick person already transmits the disease to those who come into contact with him even before it is detected.
The disease, unless endowed with the means of attention, shows no tendency to abate, but continues indefinitely.
Treatment:
Sulfur 1 especially scabies. It can be taken internally or externally. Internal remedies alone are not effective for getting rid of insect scabies, especially when they are used in low doses. dilutions
The application of Sulfur is accepted in early diseases and is also beneficial. A dose of sulfur should be administered three times a day for about two weeks. An external application of some specially treated scabies should also be used.
If, even after two weeks, the symptoms do not subside, Mercury viv. it must be given once at night and again in the morning for ten days, as Carbo veg. for several ten days, and finally the liver of sulfur must be used.